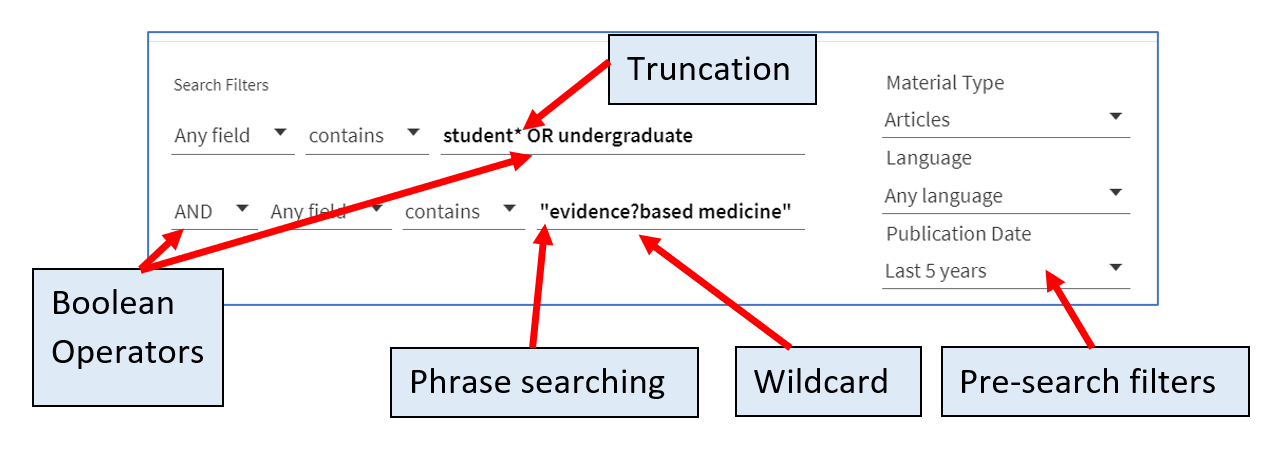
If you are comfortable using them, the Library Search supports Boolean operators, nesting, and truncation.
Boolean operators allow you to combine search terms and can make your search more precise. They are added into a search string in uppercase.
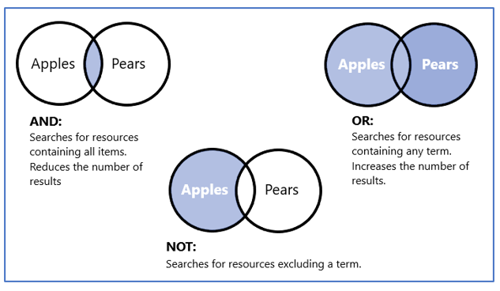
AND narrows the search by returning results with only two or more search terms. For example, apples AND pears.
OR expands the search by returning results with any of two or more search terms For example, apples OR pears.
NOT will return results containing one of two or more search terms. For example, apples NOT pears.
When using a mix of these operators remember that the search string will be looked at from left-to-right.
Using parentheses ( ) allows you to group search terms and alter the order of precedence.
Searching for phrases using quotation marks, e.g. “social media” will combine words into a single term.
The Library Search also supports truncation using the * symbol.
For example, searching for nurs* will find nurse, nurses, nursed, nursing, but also nursery.
You can use the ? symbol as a wildcard if you're unsure of a spelling or if there is a known spelling variation.
For example, organi?ation will retrieve results including organisation and organization.
You can change the scope of your search by selecting a search filter from the drop-down lists, allowing you to search only books, e-books, journals, e-journals or articles.
Example in simple search

Example in advanced search